Pressure Regulator Working
Pressure regulator working
Pressure regulators contain three important components that help them regulate pressure:
- A control element, including a seat and poppet. The seat helps contain pressure and prevents fluid from leaking to the opposite side of the regulator when flow is closed. Together with the seat, the poppet completes the sealing process while a system is flowing.
- A sensing element, typically a diaphragm or piston. The sensing element allows the poppet to rise and fall in the seat, controlling inlet or outlet pressure.
- A loading element. Regulators may be spring-loaded or dome-loaded, depending on the application. The loading element applies a downward, balancing force on top of the diaphragm.
These elements work together to create the desired pressure control. The piston or diaphragm senses upstream (inlet) pressure and downstream (outlet) pressure. The sensing element then tries to find a balance with the set force from the loading element, which is adjusted by user via a handle or other turning mechanism. The sensing element will allow the poppet to either open or close from the seat. These elements work together to remain in balance and achieve set pressure. If one changes, some other force must also change to restore balance.
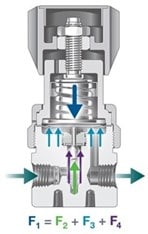
In pressure-reducing regulators, four different forces must be balanced, as shown in Figure 1. These include loading force (F1), inlet spring force (F2), outlet pressure force (F3), and inlet pressure force (F4). Total loading force must be equal to the combination of inlet spring force, outlet pressure force, and inlet pressure force.
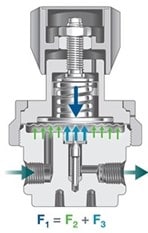
Back-pressure regulators function similarly. They must balance spring force (F1), inlet pressure force (F2), and outlet pressure force (F3), as shown in Figure 2. Here, the spring force must equal the combined force of the inlet pressure force and the outlet pressure force.
Need more Information or looking for a specific regulator?
Just fill in the below form and we will come back at the earliest