Best Practices for Hose Installation and Use
Best Practices for Hose Installation and Use
Inspection
Establish an inspection schedule based on system application and replacement history.
Electrostatic Discharge
Static electricity can be generated by fluid passing through the hose. Select hose with sufficient conductivity to ground the static electric charge and allow static dissipation. If static electricity generation is possible within an application, choose static dissipative hose and properly ground to earth.
Vibration
Evaluate amount of system vibration when selecting a hose. Metal hose may not be appropriate for systems with constant or severe vibration.
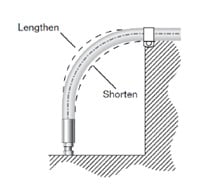
Length
Take into consideration hose movement, system pressurization, and thermal expansion when determining hose length. Installing hose that does not have sufficient length to accommodate these factors may reduce hose life.
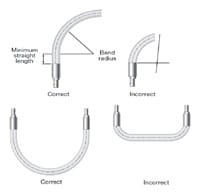
Minimum Bend Radius
Follow minimum bend radius requirements for your hose. Installing hose with smaller bends may kink the hose and reduce its life. Hose rupture or leakage may result from bending too close to the hose/fitting connection.
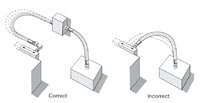
Hose Strain
Elbows and adapters can be used to relieve hose strain.

Motion Absorption
Distribute movement and prevent bends smaller than the hose's minimum bend radius by providing sufficient hose length.
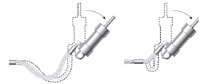
Machine Tolerance
Allow for changes in length resulting from machine motion and tolerances.

System Pressure Changes
Allow sufficient hose length to accommodate changing system pressures. Do not connect high- and low pressure hoses.
Bending in One Plane
Avoid twisting the hose by bending it in one plane only. For a compound bend, use multiple hose pieces or other isolation methods.
Need more Information or looking for a specific hose?
Just fill in the below form and we will come back at the earliest